Birth of Carl Sandburg
Pulitzer Prize-winning author Carl Sandburg was born on January 6, 1878, in Galesburg, Illinois. He wrote his own “American fairytales” as well as children’s books and biographies on Abraham Lincoln.
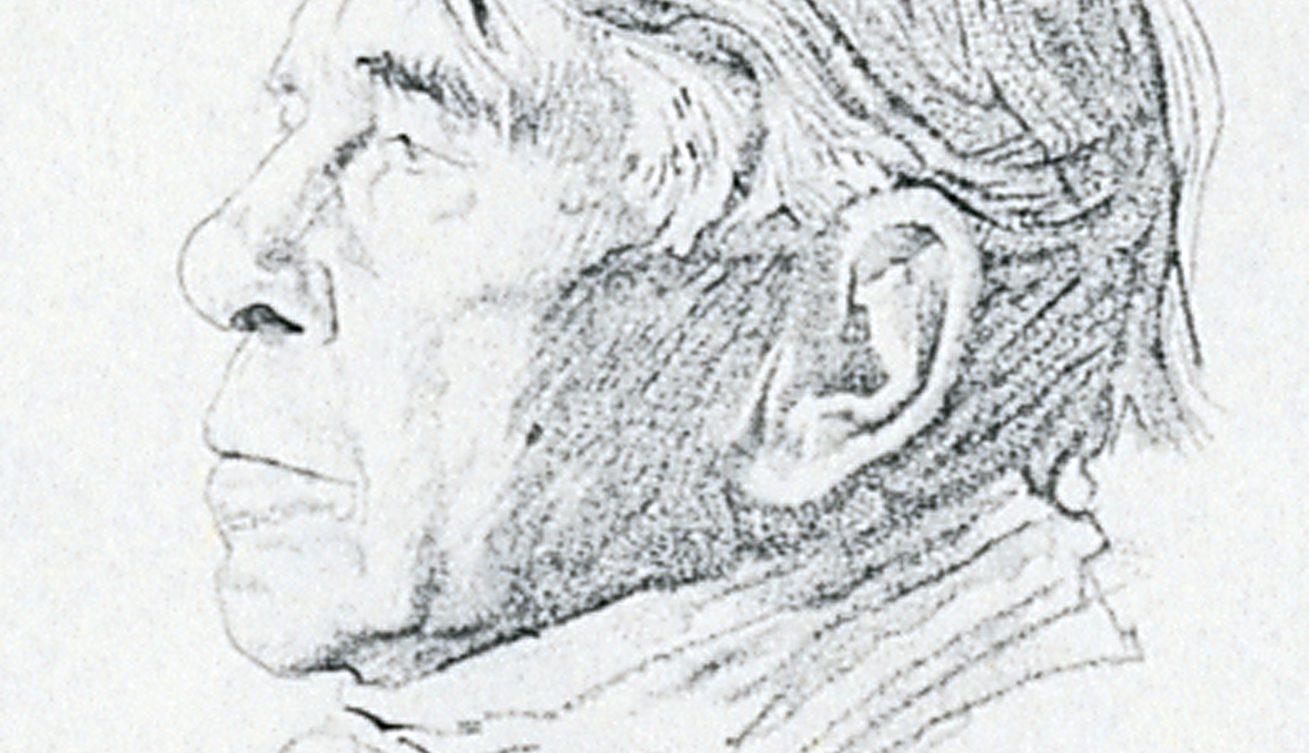

Pulitzer Prize-winning author Carl Sandburg was born on January 6, 1878, in Galesburg, Illinois. He wrote his own “American fairytales” as well as children’s books and biographies on Abraham Lincoln.
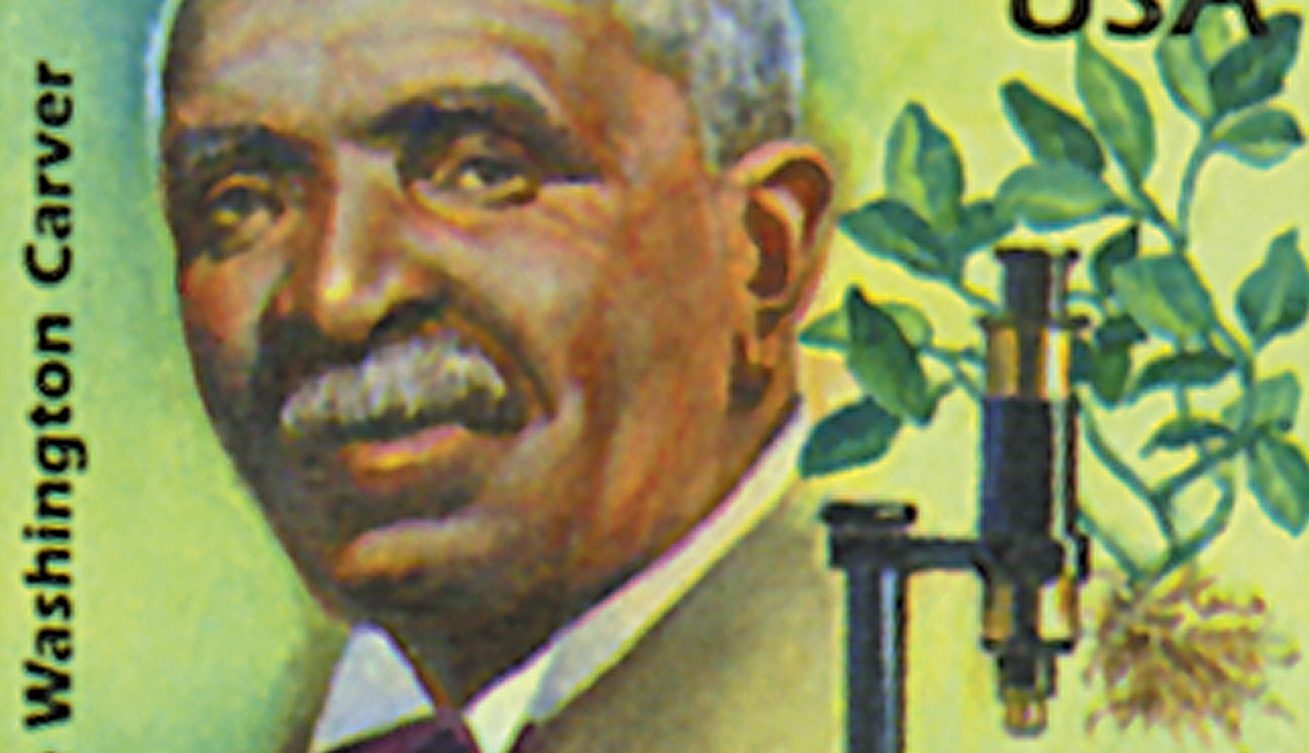

Botanist and inventor George Washington Carver died on January 5, 1943, in Tuskegee, Alabama. Carver worked to help poor Southern farmers and is most famous for developing more than 300 uses for peanuts, earning the nickname, “Peanut Man.”

Nurse, businesswoman, and philanthropist Nellie Cashman died on January 4, 1925, in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada. Spending much of her life running boarding houses near mining camps and caring for sick miners, she became known as the “Miners’ Angel.”
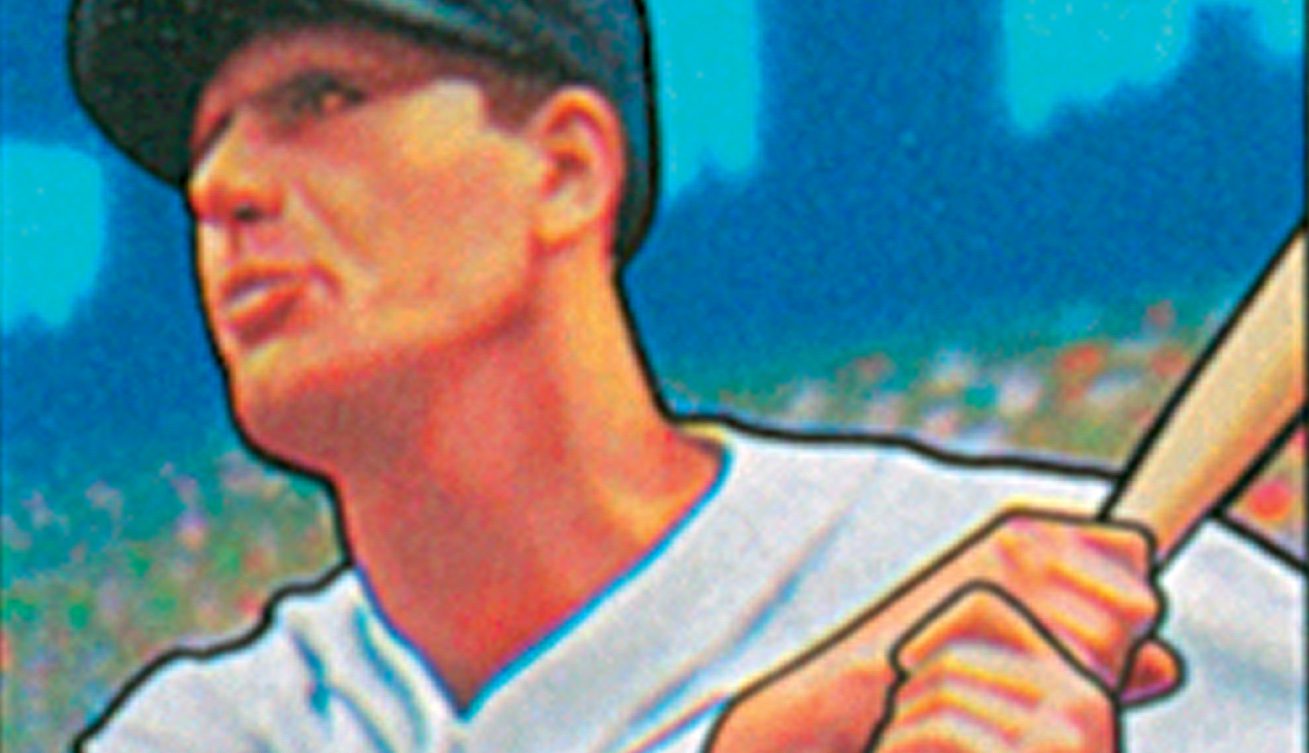

On January 1, 1911, Henry Benjamin Greenberg was born in New York City, New York. One of the greatest sluggers in baseball history, he put his career on hold to serve 47 months with the Army during World War II, the most of any major league player.
On December 31, 1903, Times Square hosted its first-ever New Year’s Eve Celebration. It’s one of the largest and longest-running New Year’s Eve celebrations in the world.
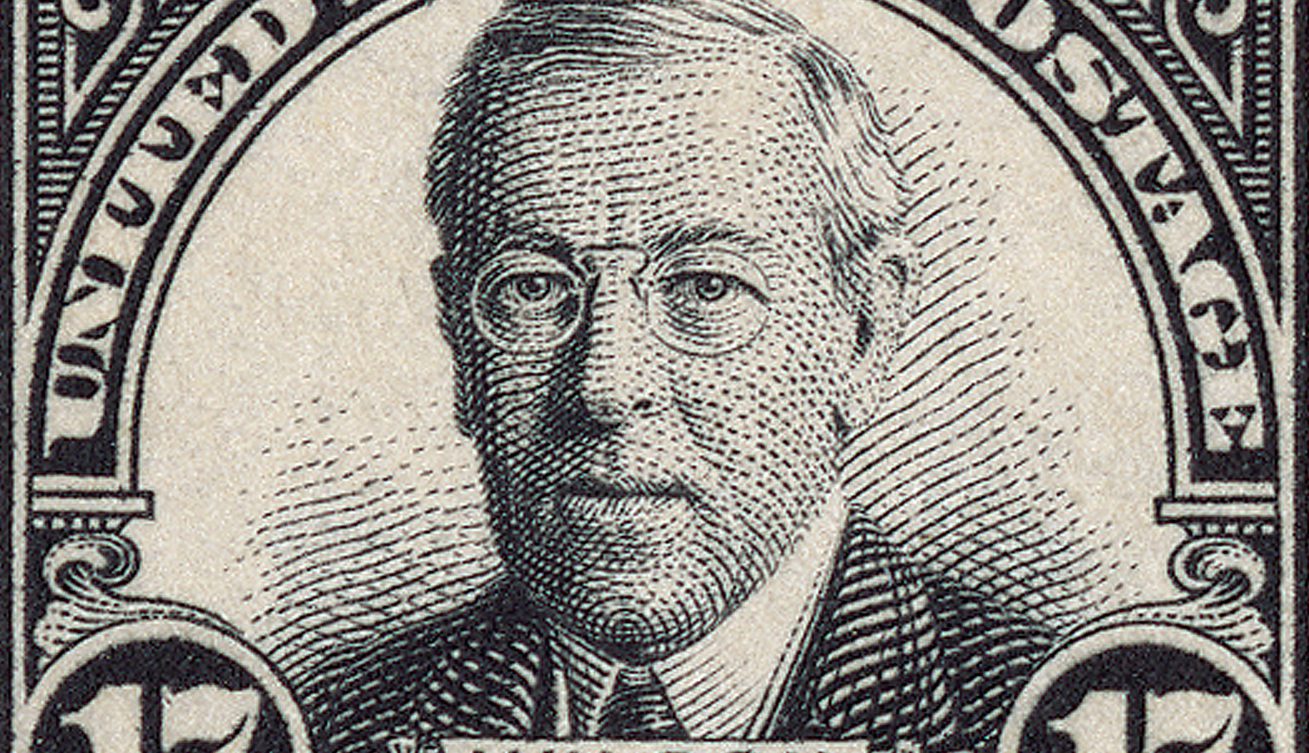

Thomas Woodrow Wilson was born on December 28, 1856, in Staunton, Virginia. As America’s 28th president, he let America into World War I and is considered the architect of the League of Nations.
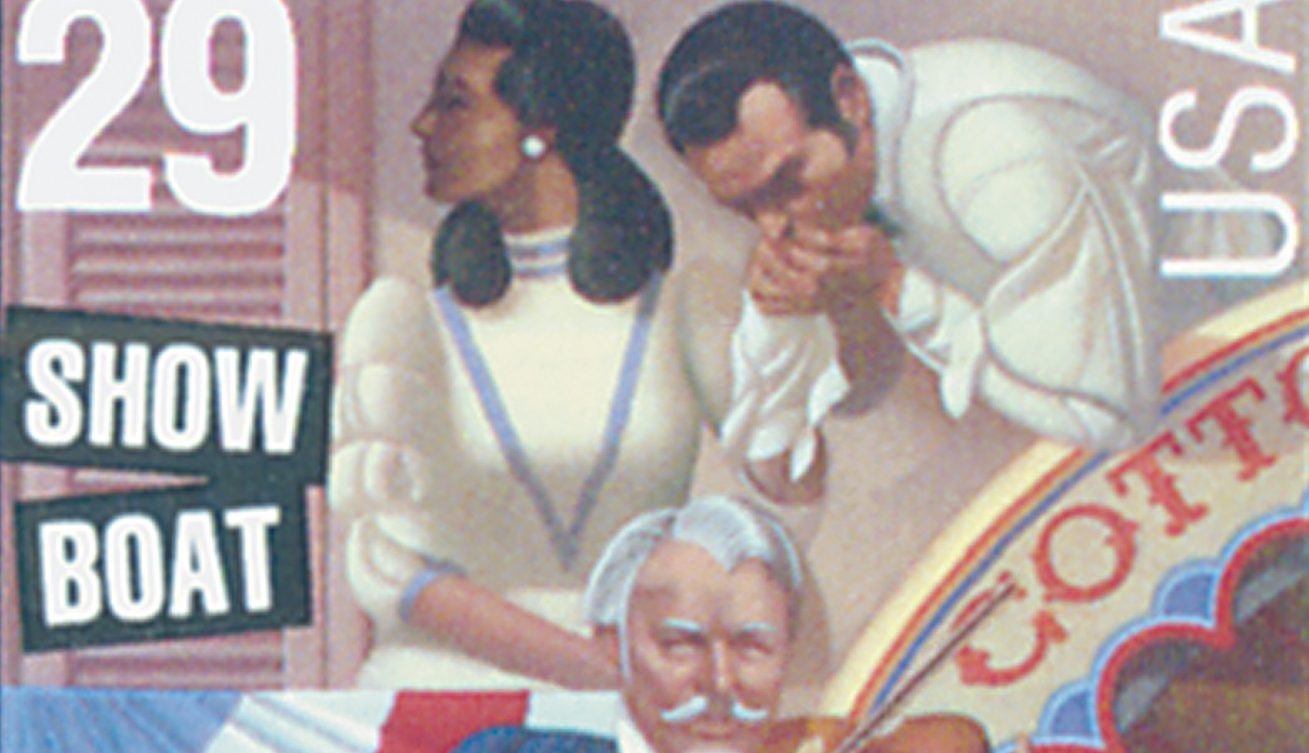

On December 27, 1927, the musical Show Boat debuted at Broadway’s Ziegfeld Theater. The play was hailed as an artistic masterpiece and the film was a box office hit.
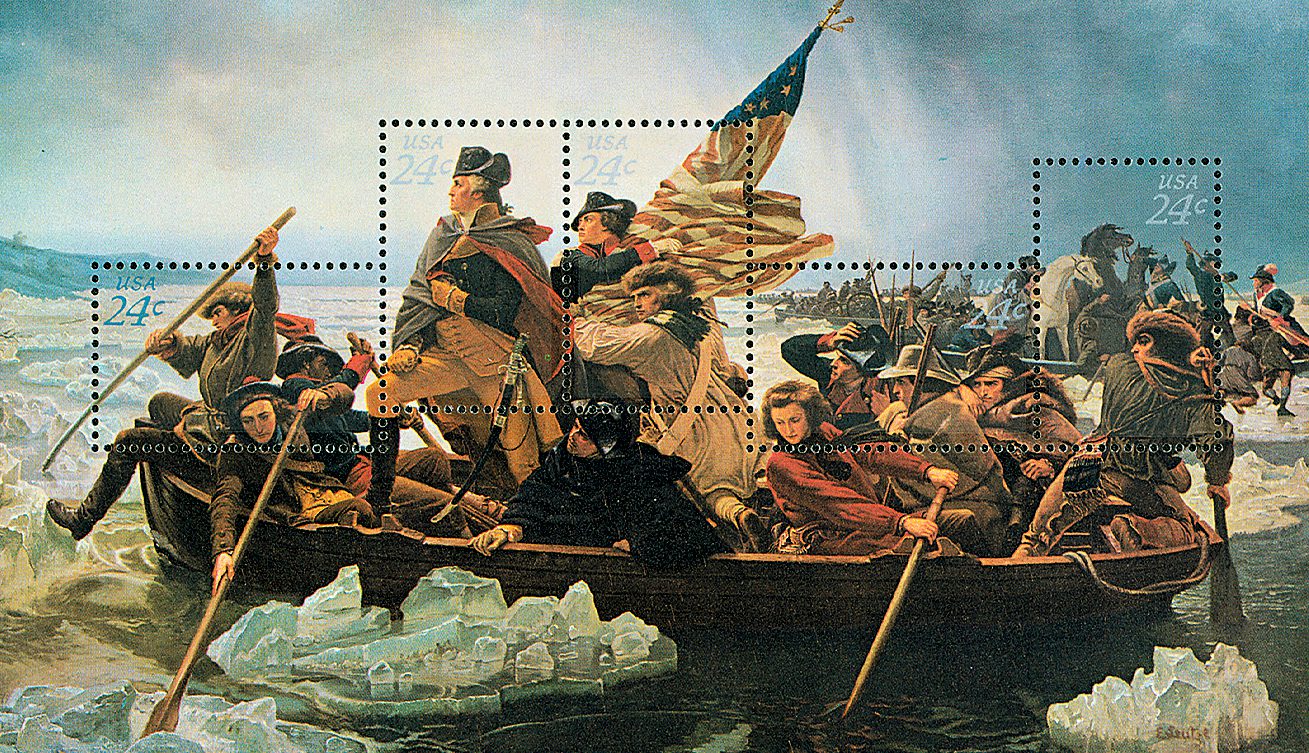

On the night of December 25, 1776, George Washington led his men across the Delaware River in a surprise attack on the British. Their victory at Trenton was a significant morale booster – encouraging troops to reenlist and convincing new recruits to join the fight.
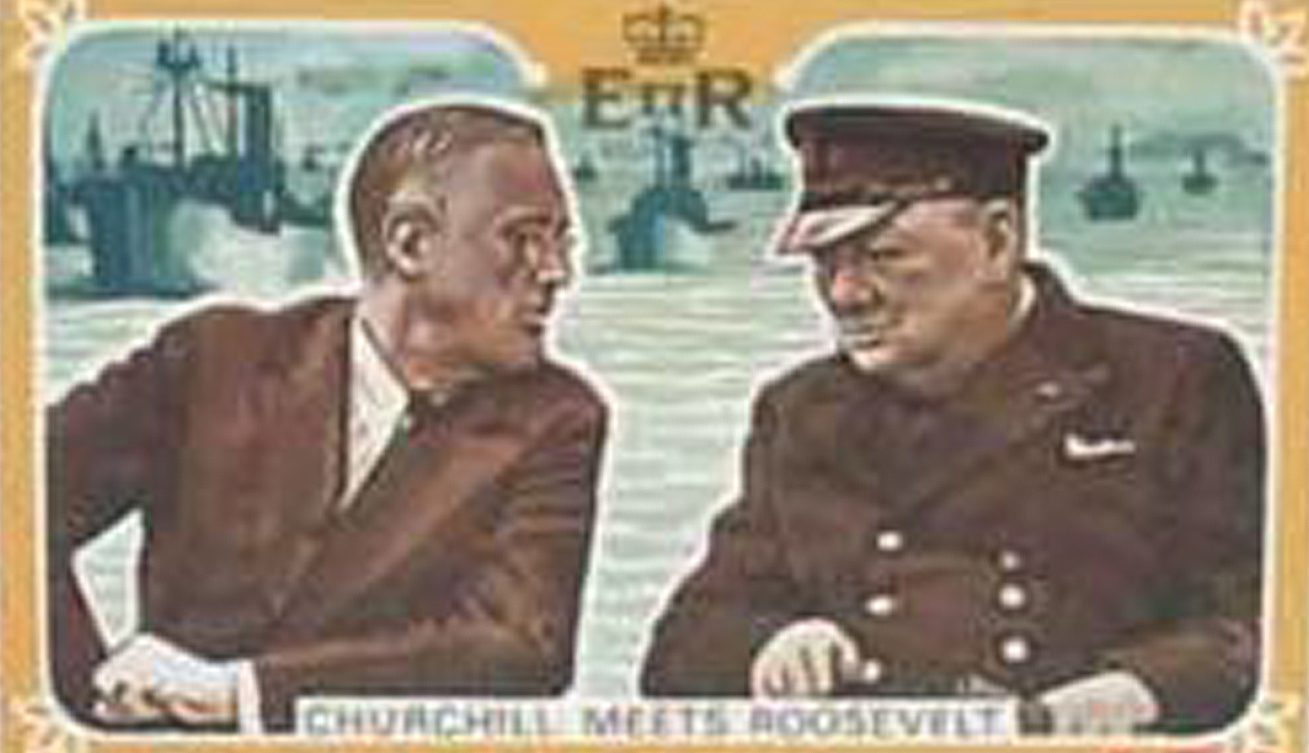

On December 22, 1941, US and British leaders met at the White House for the first time to discuss military strategy for World War II. The Arcadia Conference, as it was known, established Allied goals for the war and laid the groundwork for the United Nations.